









DIABETeS
Diabetes “Pandemic of the 21st century”
Most recent report published by the international diabetes federation IDF on 12, 2019 indicate the following statistics or findings below:
(from the biennial international report, most recently published by the International Diabetes Federation IDF on 12/2019)
- 1 in 11 adults have diabetes (Approximately 463 million people worldwide)
In 2019, 4.2 million people died from the effects of diabetes (this means that one person dies from the effects of diabetes every 8 seconds)
Unreported number 1 out of 2 people has not yet been diagnosed with diabetes)
1 in 6 pregnancies is affected by hyperglycemia (gestational diabetes)
- Over 1 million children and adolescents suffer from type I diabetes
- 1 in 5 people with diabetes are over 65 years old (Approximately 93 million people)
- Over 396 million people aged 19 to 64 suffer from diabetes
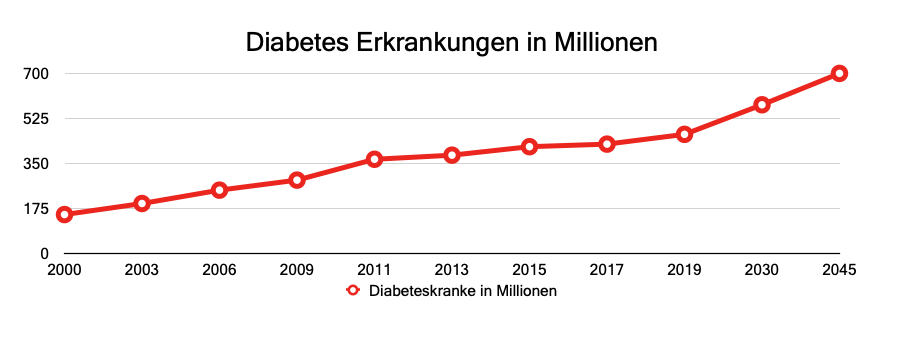
- It is predicted that by 2030 we will have 578 million people with diabetes and by 2045 there will be 700 million people
Type I diabetes mellitus
Clinical Symptoms:
- The pancreas (pancreas) no longer or insufficiently produces the hormone insulin.
- Type 1 diabetes is diagnosed diagnostically when 80% of insulin production has already been discontinued or is missing.
- 90% of the patients have no family disposition.
Symptoms:
- Increased urge to urinate (polyuria) with increased thirst (polydipsia).
- Other symptoms reported include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fatigue, ketoacidosis.
The patients are mainly children, adolescents and young adults. Since the pancreas does not produce the hormone insulin sufficiently or not at all, sufferers are dependent on insulin for a lifelong injection.
Causes:
An autoimmune reaction is assumed in which the immune system attacks the body’s own insulin-producing beta cells.
There are beta and alpha cells in the pancreas. The pancreas is responsible for delivering insulin and glucagon to the bloodstream. Both hormones regulate blood sugar and carbohydrate metabolism. Glucagon and insulin are so-called opponents.
Laboratoroy test results:
Fasting plasma glucose value ≥ 126 mg / dl (7.0 mmol / l)
Occasional plasma glucose value ≥ 200 mg / dl (11.1 mmol / l)
Plasma glucose value two hours after 75 g of glucose in the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT = sugar exposure test) ≥ 200 mg / dl (11.1 mmol / l)
HbA1c value (so-called long-term value) ≥ 6.5%
Special forms of Diabetes mellitus Typ I:
Diabetes melitus type I b (idiopathic type I diabetes):
In this special form, no antibodies against the insulin or other parts of the beta cells are detectable. So far, the cause is missing.
Type I Diabetes mellitus LADA (latent autoimmune diabetes in adults):
Adults of normal weight who have particularly mild symptoms of type I and type II diabetes are affected. The patients have characteristic antibodies. Treatment usually begins with taking tablets, but ends with insulin injection. Type II diabetes is often misdiagnosed at the beginning of the disease.
Type II Diabetes
Type II diabetes is the most common of all diabetes. Currently, 462 million people are affected worldwide. This disease is exploding close to and has tripled in the past 20 years.
If you look at where the development looks like the causes, it quickly becomes clear that it is a disease of civilization.
In the meantime, diabetes is even diagnosed in animals. However, it should be noted that these are only pets that are fed by human hands.
Clinical Symptoms:
The pancreas produces insulin, but the body cells lose their sensitivity, which leads to insulin resistance in the long term.
The release of insulin from the cells is disturbed and the pancreas tries to compensate for this and produces more and more insulin. Despite high insulin release, less and less glucose gets into the body cells. Triggering factors include:
- Obesity / overweight
- Lack of movement
- Quantitatively high intake of macronutrients (empty carbohydrates, bad fats and industrial sugar
- Long-lasting micronutrient deficits (lack of vitamins & trace elements)
- Elevated blood fat levels and high blood pressure are often associated with prediabetes or diabetes (metabolic syndrome).
- A family disposition can be observed
Diagnosis:
It is often a long process until the diagnosis is made, in contrast to type I diabetes, since the disease develops gradually and symptoms gradually appear.
Treatment:
In addition to a change in diet and weight loss, the patient is treated with metformin hydrochloride. It is taken with meals. The active ingredient inhibits the absorption of glucose in the intestine and at the same time increases the absorption into the cells. Insulin resistance is reduced.
The active ingredient lowers the vitamin B12 level, so it is important that the vitamin is measured and supplemented here.
Micronutrient requirements for diabetes:
- Zinc 20-40 mg
- Chromium 100-200 ug
- Magnesium 300-600 mg
- Vitamin C 1-2 g
- Fat acids Omega 3 2-3 g
- Vitamin E 400 I.E.
- Alpha Lipoic Acid 600 mg
- Vitamin B complex
- L-arginine base 6-8 g
